Free Shipping On All Orders Over $150.
Cat Pneumonia with Wheezing Cough: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
How to treat pneumonia in cats with wheezing cough is a crucial concern for pet owners, especially during seasonal changes when feline health can be compromised. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and effective treatment options can make a significant difference in your cat's recovery and overall well-being. In this article, we will explore various aspects of cat pneumonia treatment for wheezing and coughing, including home remedies, vet-approved treatments, and preventive measures to help keep your furry friend healthy.
The Breeds Most Prone to Pneumonia

While all cats can be susceptible to pneumonia, certain breeds exhibit a higher tendency towards respiratory issues. This increased risk can be attributed to anatomical features, pre-existing health conditions, or environmental factors affecting their immune systems.
Brachycephalic Breeds
Brachycephalic breeds like Persian, Ragdoll, and Himalayan cats are particularly vulnerable to respiratory infections. Their flat facial structure leads to narrower airways, making it harder to breathe efficiently. Consequently, they face an elevated risk of developing pneumonia, especially if they already have underlying respiratory issues.
These breeds require specialized care and monitoring to prevent infection. Pet owners should pay close attention to any coughing or wheezing sounds, as early detection can substantially improve recovery outcomes.
Kittens and Senior Cats
Kittens aged between 1-3 months and senior cats often possess weaker immune systems, making them more prone to pneumonia. Kittens, still developing their defenses against infections, may succumb quickly to illnesses like pneumonia. Similarly, elderly cats often have age-related health problems that further compromise their ability to fight off infections.
Understanding the vulnerabilities within these groups can empower owners to take proactive measures. Regular veterinary check-ups and vaccinations are essential to help bolster their immune systems and mitigate risks.
Ill Cats
Cats suffering from other illnesses or those with compromised immune systems are also at heightened risk for pneumonia. Conditions such as diabetes, cancer, or chronic kidney disease weaken the immune response, making it easier for infections to take hold.
If you have a cat with existing health concerns, it's essential to monitor its respiratory health closely. An increase in coughing, wheezing, or general lethargy may signify the onset of pneumonia, prompting immediate veterinary consultation.
Causes of Pneumonia in Cats
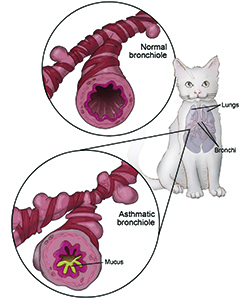
Understanding the various causes of pneumonia in cats is vital for effective treatment and prevention. This section explores the most common types of pneumonia, namely bacterial, fungal, and aspiration pneumonia.
Bacterial Pneumonia
Bacterial pneumonia occurs when bacteria invade the lungs, leading to inflammation and fluid accumulation. Common culprits include Bordetella bronchiseptica, Pasteurella, and Chlamydia felis. These bacteria can enter through various means, including inhalation or bloodstream infection.
In many cases, bacterial pneumonia develops after a viral infection weakens the cat’s immune system. Thus, maintaining your cat’s overall health is crucial in preventing bacterial infections. Regular vaccinations and avoiding exposure to known pathogens can greatly reduce the risk.
Fungal Pneumonia
Fungal pneumonia is less common but poses significant health risks, especially for cats with weakened immune systems. Different fungi can cause infections, most notably Cryptococcus, Histoplasma, and Blastomyces. These spores typically reside in soil or decaying organic matter, increasing the chances of exposure for outdoor cats.
Preventing fungal pneumonia necessitates careful monitoring of your cat's environment, particularly in areas where these fungi thrive. Regular veterinary visits can help assess your cat's immune status and implement preventative measures.
Aspiration Pneumonia
Aspiration pneumonia occurs when a cat inhales foreign substances, such as food, vomit, or chemicals, into its lungs. This can lead to inflammation, infection, and subsequent respiratory complications. Factors such as obesity or neurological disorders may heighten the risk of aspiration since they can affect swallowing mechanisms.
Owners must remain vigilant during feeding times, ensuring their cat eats in a calm environment. Additionally, minimizing exposure to potential toxins and keeping the living space free of hazardous materials can help protect against aspiration pneumonia.
Signs Your Cat Has Pneumonia
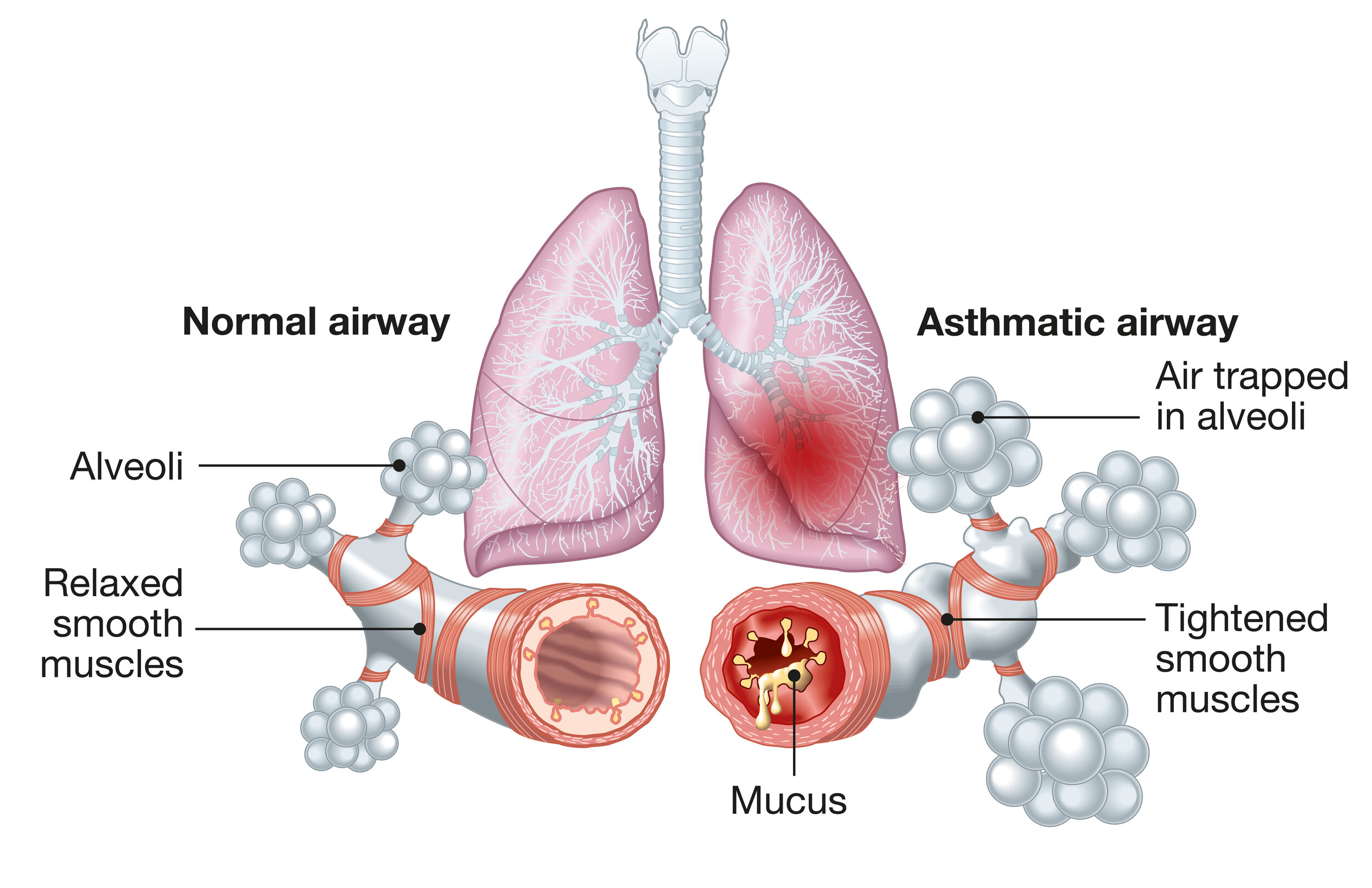
Recognizing the signs of pneumonia in cats is paramount for prompt intervention. While some symptoms are distinct, others may appear subtle, requiring keen observation from pet owners.
Respiratory Distress
Difficulty breathing and wheezing are hallmark signs of pneumonia. Cats may show shallow, rapid breaths, often accompanied by audible wheezing sounds. If your cat exhibits these symptoms, it could indicate restricted airflow caused by fluid buildup in the lungs.
Monitoring your cat's breathing pattern is essential. If you notice any significant changes, consult your veterinarian immediately to rule out pneumonia.
Cough
A persistent or sudden cough is another common symptom of pneumonia. Depending on the severity of the condition, the cough can range from mild to severe and may produce mucus or blood. It's important to differentiate between normal cat behavior and an alarming cough indicative of respiratory illness.
Documenting the frequency and nature of the cough can provide essential information for your veterinarian. Seek professional help if the cough persists for an extended period or worsens.
Other Symptoms
Several other symptoms may accompany pneumonia, ranging from mild discomfort to severe distress:
- Lethargy: An early sign of illness, lethargy can indicate that your cat is not feeling well and may need medical attention.
- Loss of Appetite: A decrease in food intake can signify various health issues, including pneumonia. Pay extra attention to your cat's eating habits, as this can impact recovery.
- Nasal Discharge: Clear or colored nasal discharge may signal respiratory infection. While it might seem minor, it can escalate into a more serious issue if left untreated.
Diagnosing Pneumonia in Cats
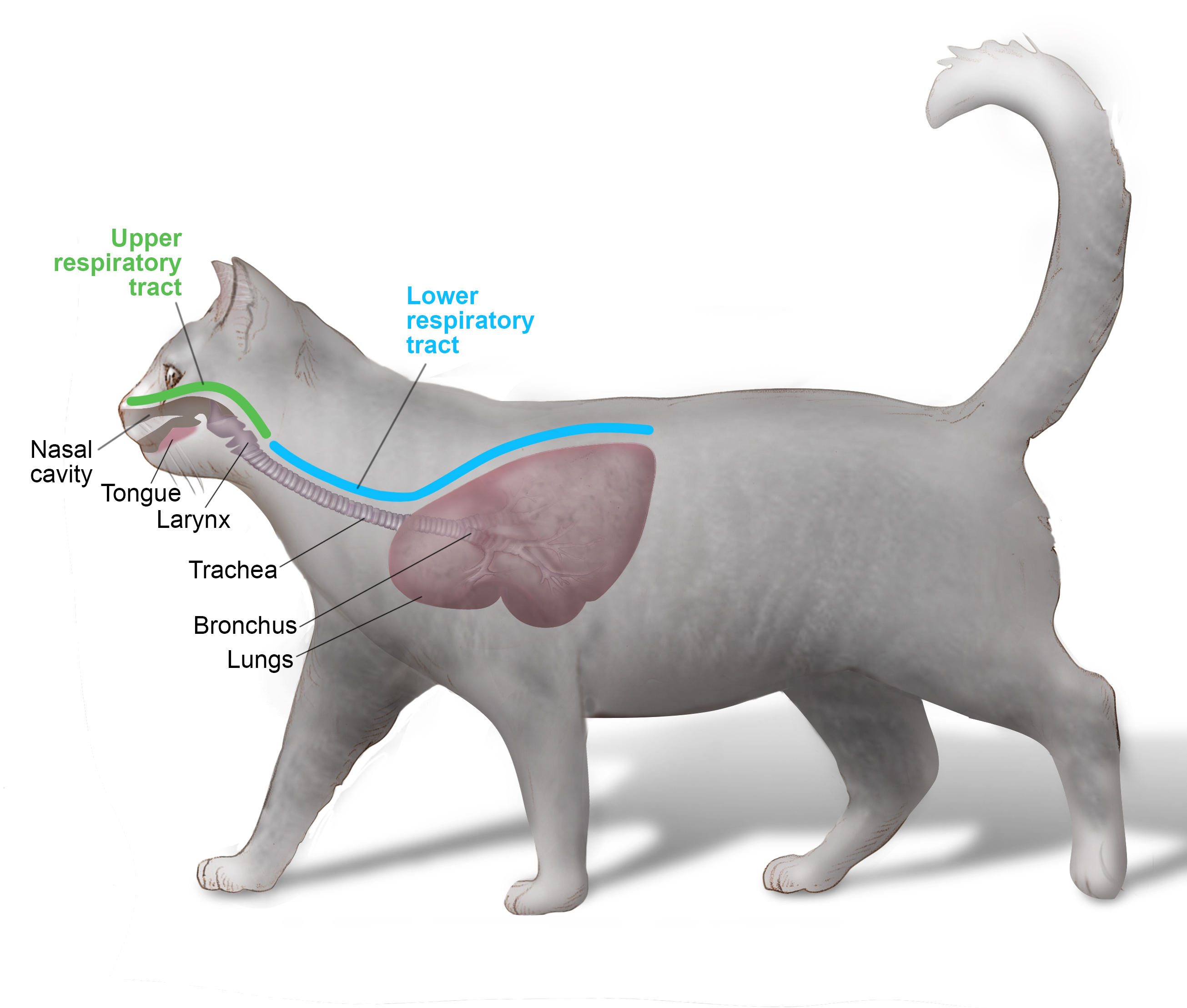
Diagnosing pneumonia involves a thorough evaluation to determine the underlying cause and severity of the condition. This process typically includes a combination of history-taking, physical examination, and diagnostic tests.
Medical History and Physical Examination
The first step in diagnosing pneumonia is gathering detailed information about your cat's medical history. Your veterinarian will ask about previous illnesses, vaccination status, and any recent exposure to sick animals. A physical examination will follow, focusing on assessing respiratory sounds and overall health.
Listening to your cat's lungs with a stethoscope can reveal abnormalities such as crackling or wheezing, which are indicative of pneumonia. Based on initial findings, your vet may recommend further tests to confirm the diagnosis.
Blood Tests
Blood tests play a crucial role in diagnosing pneumonia. They can help identify the presence of infection by measuring white blood cell counts. Elevated levels may suggest a bacterial infection, while other markers can indicate possible viral or fungal involvement.
Additionally, blood tests can help ascertain your cat's overall health, guiding treatment decisions and future management strategies.
Radiographs (X-rays)
Chest X-rays are invaluable for visualizing issues within the lungs. They can reveal the extent of pneumonia, fluid accumulation, and any underlying structural problems. Your veterinarian may use these images to determine the best course of action for treatment.
It's important to note that X-ray results should be evaluated alongside clinical signs and laboratory findings, as they collectively provide a comprehensive understanding of your cat's condition.
Additional Diagnostic Tests
After confirming pneumonia, additional diagnostic tests may be necessary to determine the specific causative agent and tailor the most effective treatment plan.
Fecal Examination
A fecal examination can help identify the presence of parasites, which can contribute to respiratory issues. Certain parasites can cause systemic infections that may lead to pneumonia. Regular deworming and monitoring can help prevent these complications.
Viral Testing
Testing for feline viruses, such as FIV (Feline Immunodeficiency Virus) and FeLV (Feline Leukemia Virus), may be warranted in cases where viral infections are suspected. These viruses can severely compromise a cat's immune system, making pneumonia more likely.
Cultures and Sensitivity Testing
In some cases, obtaining cultures from the trachea or lung fluid may help identify the specific bacteria causing the pneumonia. This information is essential for selecting the most effective antibiotics, ensuring a targeted approach to treatment.
Treatment Options for Pneumonia in Cats
Once diagnosed, treating pneumonia requires a comprehensive approach tailored to the individual cat's needs. Various methods can facilitate recovery, including medications, supportive care, and lifestyle adjustments.
Antibiotics
Bacterial pneumonia typically necessitates antibiotic therapy. Your veterinarian may prescribe a combination of antibiotics, tailored to combat the specific bacteria identified through testing. Common choices may include Penicillin combined with Kanamycin or Gentamicin.
It's critical to administer medications exactly as prescribed and complete the full course, even if your cat starts showing signs of improvement. Stopping prematurely may allow remaining bacteria to multiply and cause a resurgence of illness.
Antifungal Medications
If fungal pneumonia is diagnosed, antifungal medications will be initiated. The specific drug prescribed will depend on the type of fungi identified. Close monitoring is essential, as some antifungal medications can have side effects.
Providing a safe and stress-free environment can enhance your cat's recovery while undergoing antifungal treatment. Regular follow-up appointments will help gauge effectiveness and adjust treatment plans as needed.
Supportive Care
Supportive care plays a pivotal role in the treatment of pneumonia, especially in severe cases. Ensuring proper hydration and nutrition is vital for recovery. Offer your cat enticing, easily digestible foods that will encourage them to eat.
Additionally, maintaining a clean and comfortable environment enhances recovery. Use a humidifier to alleviate respiratory discomfort, and keep your cat's space free from allergens and irritants.
Caring for a Cat with Pneumonia
Caring for a cat with pneumonia involves active monitoring and implementing preventive measures to promote healing. Here are some key considerations for responsible pet owners.
Monitoring Symptoms
Keep track of your cat's symptoms and any changes in behavior. Document their breathing patterns, appetite, and energy levels. If symptoms worsen or new symptoms arise, consult your veterinarian promptly for reassessment.
Maintain regular communication with your vet regarding your cat’s progress to ensure the treatment plan remains effective. Open dialogue fosters collaboration between you and your veterinarian, ultimately benefiting your cat's health.
Administering Medications
Ensure that all prescribed medications are given at the correct dosage and schedule. Medication adherence is crucial for achieving the desired therapeutic outcomes. Create reminders or use pill organizers to assist in managing complex regimens.
Don't hesitate to contact your vet for guidance if you encounter difficulties administering medications. They can provide alternatives or tips to facilitate the process.
Creating a Comfortable Environment
A conducive environment is vital for facilitating recovery. Designate a quiet and cozy space where your cat can rest without disturbance. Keep the temperature moderate to avoid extremes that may exacerbate respiratory distress.
Consider using a warm compress on your cat’s chest to help ease discomfort associated with pneumonia. Gentle handling while providing affection can help soothe your cat during this challenging period.
Preventing Pneumonia in Cats
Prevention is the cornerstone of responsible pet ownership, especially regarding conditions like pneumonia that can escalate into serious health threats.
Vaccination
Vaccinations are an integral part of preventive healthcare for cats. Ensure your cat is up-to-date on vaccinations against respiratory viruses and bacterial infections. Consult your veterinarian regarding the appropriate vaccine schedule for your cat's age and lifestyle.
Regular vaccinations will strengthen your cat's immune system against pathogens that could trigger pneumonia, significantly reducing susceptibility.
Environmental Control
Creating a safe and healthy living environment is essential for disease prevention. Limit exposure to known allergens and irritants, such as smoke or strong perfumes, which can compromise respiratory health.
Monitor your cat's interactions with other animals, particularly those exhibiting signs of illness. Isolating sick pets can curb the spread of infections among household members.
Regular Veterinary Check-ups
Routine veterinary examinations enable early detection of potential health issues before they escalate. Regular assessments can highlight any concerning symptoms and allow for timely intervention.
Moreover, discussing your cat's lifestyle and behavior with your veterinarian can yield personalized recommendations for preventive care based on specific risks faced by your pet.
The Importance of Recognizing Upper Respiratory Infections
Upper respiratory infections are common amongst cats and can lay the groundwork for more severe respiratory issues, such as pneumonia. Understanding how to recognize and address these infections can mitigate risks.
Signs of Upper Respiratory Infections
Signs of upper respiratory infections typically mirror those seen in humans, including sneezing, nasal congestion, and watery eyes. It’s crucial to recognize these symptoms early and initiate care to prevent progression to pneumonia.
Infected cats may also exhibit coughing and increased vocalization due to discomfort. Prompt veterinary intervention can guide treatment and safeguard against severe complications.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing upper respiratory infections often involves a physical examination and consideration of your cat's history. Your veterinarian may recommend supportive care, including steam therapy and hydration, to ease symptoms.
Antibiotic therapy may be required if a bacterial infection is suspected. However, many upper respiratory infections are viral and often resolve independently with proper care and time.
Prevention Strategies
Implementing preventive measures for upper respiratory infections can significantly reduce the risk of subsequent pneumonia. Vaccinating against common pathogens and ensuring your cat is healthy and stress-free can bolster their defenses.
Keeping your cat indoors can minimize exposure to airborne pathogens, while good hygiene practices—such as cleaning litter boxes regularly—can reduce the likelihood of infection.
Conclusion
In summary, navigating the complexities of pneumonia in cats requires vigilance, understanding, and prompt action. Learning how to treat pneumonia in cats with wheezing cough encompasses recognizing symptoms, seeking veterinary assistance, and adhering to treatment protocols. By staying informed about cat pneumonia treatment for wheezing and coughing, pet owners can foster healthier environments, ultimately enhancing their companions' lives. Remember, prioritizing routine veterinary care and addressing upper respiratory infections proactively can significantly reduce the risk of pneumonia for your beloved feline friends.
0 comment
Be the first to comment