Free Shipping On All Orders Over $150.
Causes and Prevention of Jaundice in Cats
Jaundice in cats is a serious health issue that warrants immediate attention from pet owners. This condition, characterized by the yellowing of the skin and eyes, is often a sign of underlying medical problems, especially related to liver function. Knowing how to recognize the signs and understand the causes can be crucial for timely treatment.
Jaundice in Cats

Jaundice in cats, also known as icterus, occurs when there is an accumulation of bilirubin in the bloodstream. Bilirubin is a yellow pigment formed during the normal breakdown of red blood cells. When healthy, the liver processes this pigment, but if the liver is compromised, bilirubin levels rise, leading to noticeable symptoms.
Cats are particularly sensitive to changes in their liver function, which can result from various factors including infections, toxins, or metabolic diseases. The color change associated with jaundice is typically most visible in the cat’s eyes, skin, and mucous membranes. Recognizing these signs is essential for pet owners who wish to take proactive measures regarding their feline companion's health.
The consequences of untreated jaundice in cats can be severe, potentially leading to liver failure or other serious complications. Hence, understanding the symptoms and seeking veterinary care promptly is vital.
What Happens in the Body During Jaundice?

When a cat's liver is unable to process bilirubin effectively, it leads to increased levels in the blood. This condition can occur for several reasons, ranging from liver disease to hemolysis (the breakdown of red blood cells). If left unchecked, the accumulating bilirubin can cause damage not only to the liver but also to other organs.
An important aspect of understanding jaundice is recognizing that it's a symptom rather than a standalone disease. Various underlying conditions may lead to jaundice, which means thorough diagnostics are often necessary to determine the root cause.
Recognizing Signs of Jaundice
Detecting jaundice might seem straightforward due to the characteristic yellowing, yet many owners may miss early signs. Often, you may first notice a subtle yellowing of the gums or the whites of the eyes before it becomes evident in the skin. Other signs accompanying jaundice may include lethargy, loss of appetite, and vomiting, all of which are indicators that your cat requires immediate veterinary attention.
Being aware of these symptoms helps owners act quickly. Early intervention can significantly improve treatment outcomes, making it essential for responsible pet ownership.
Feline Jaundice Causes
Understanding the feline jaundice causes is critical for effective diagnosis and treatment. Jaundice is not a disease itself but a symptom indicative of several potential health issues affecting the liver or the body's ability to process bilirubin.
Liver Disease
One of the primary causes of jaundice in cats is liver disease. Conditions such as hepatitis, fatty liver syndrome, or tumors can disrupt normal liver function, resulting in elevated bilirubin levels.
Liver disease can be acute or chronic, with acute cases often resulting from viral infections, toxins, or medications that have adverse effects on liver cells. Chronic liver disease may develop over time due to factors like obesity or prolonged exposure to harmful substances.
Hemolytic Anemia
Another significant cause of jaundice in cats is hemolytic anemia, a condition where red blood cells are destroyed faster than they can be produced. The rapid breakdown of red blood cells leads to an increase in bilirubin production, overwhelming the liver's ability to metabolize it.
Factors contributing to hemolytic anemia can include autoimmune disorders, reactions to certain drugs, or even infections such as feline leukemia virus (FeLV) or feline immunodeficiency virus (FIV). Identifying the specific cause of hemolytic anemia is essential for effective treatment.
Bile Duct Obstruction
Bile duct obstruction can also lead to jaundice. Just as the liver plays a role in processing bilirubin, it also produces bile, which is essential for digestion. If the bile ducts become blocked—due to gallstones, tumors, or inflammation—bilirubin cannot be properly excreted, resulting in jaundice.
Symptoms may vary depending on the severity and cause of the obstruction. Prompt veterinary intervention is necessary to address the underlying problem and restore proper liver function.
Cat Liver Disease
:strip_icc()/GettyImages-167596491-5a627cf47bb2830037dd5869.jpg)
Cat liver disease encompasses a range of conditions that can impact a cat's overall health and well-being. Understanding the intricacies of these diseases is essential for pet owners looking to safeguard their feline companions from serious health risks.
Types of Cat Liver Diseases
There are multiple types of cat liver diseases, each with distinct characteristics. Common conditions include fatty liver disease, cholangitis, and hepatic lipidosis.
Fatty liver disease, or hepatic lipidosis, is particularly prevalent among overweight cats. It occurs when excessive fat accumulates in the liver, impairing its functionality. This condition can develop rapidly, especially after periods of stress or illness that lead to decreased food intake.
Cholangitis involves inflammation of the bile ducts, which can stem from bacterial infections or autoimmune responses. This condition can cause jaundice by disrupting the flow of bile and the metabolism of bilirubin.
Risk Factors for Liver Disease
Several risk factors predispose cats to liver disease. These include age, breed, diet, and lifestyle choices. Older cats are generally more susceptible, as their organ functions decline with age. Certain breeds, such as Siamese and Burmese, may possess genetic predispositions to liver conditions.
Additionally, poor diet and sedentary lifestyles can contribute to obesity and subsequent liver issues. Educating yourself about these risk factors allows pet owners to take preventive action, potentially reducing the risk of liver-related complications.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Liver Disease
Diagnosing cat liver disease typically involves a combination of physical examinations, blood tests, and imaging studies like ultrasounds. Blood work can reveal elevated liver enzymes indicating dysfunction, while imaging helps visualize structural abnormalities.
Treatment varies widely based on the type and severity of the liver disease. Options may include dietary changes, medications, or even surgical interventions in severe cases. Comprehensive care, including regular monitoring and follow-ups, is crucial for managing liver disease effectively.
Yellow Skin in Cats
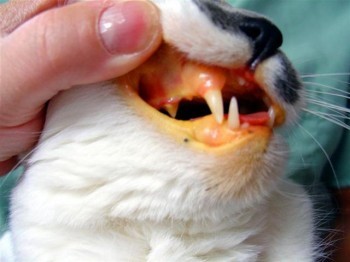
The most apparent sign of jaundice in cats is the presence of yellow skin in cats. This discoloration serves as a visual cue for pet owners and veterinarians alike, highlighting the need for further investigation into the cat's health.
How Yellow Skin Develops
Yellow skin develops when excess bilirubin builds up in the bloodstream. Under normal circumstances, bilirubin is processed by the liver and excreted via bile. However, when liver function is impaired or there is an obstruction, bilirubin levels can rise dramatically, resulting in jaundiced skin.
The yellow coloration tends to start at the ears and the inside of the mouth, gradually spreading to the rest of the body. Observing these signs can prompt pet owners to seek veterinary advice sooner rather than later.
Importance of Early Detection
Recognizing yellow skin in cats is crucial because it often signifies a serious underlying issue. Early detection can make a significant difference in treatment outcomes. If jaundice is identified alongside other symptoms like vomiting or lethargy, it’s essential to consult a veterinarian for a comprehensive evaluation.
Delaying treatment can exacerbate underlying liver conditions, leading to more severe complications. Thus, awareness and vigilance are key to ensuring long-term health for your feline friend.
The Relationship Between Diet and Skin Color
Diet can also play a surprising role in the coloration of a cat’s skin. While jaundice primarily results from liver dysfunction, certain dietary deficiencies can contribute to overall skin health. A balanced diet ensures that the liver has the nutrients necessary for optimal function.
Pet owners should consider providing high-quality, nutritionally balanced food and avoiding fillers or low-quality ingredients, which can stress the liver over time. Proactive dietary management can support liver health, potentially preventing conditions that lead to jaundice.
Feline Hepatitis Symptoms

Feline hepatitis, an inflammation of the liver, presents various symptoms, some of which overlap with those of jaundice. Recognizing feline hepatitis symptoms is essential for prompt diagnosis and treatment.
General Symptoms of Feline Hepatitis
Common symptoms of feline hepatitis include vomiting, diarrhea, loss of appetite, and lethargy. These signs can often be mistaken for a variety of other illnesses, making it challenging for pet owners to pinpoint the issue.
As the disease progresses, you may notice further symptoms like jaundice, abdominal distension, or fever. Monitoring your cat's behavior and reporting any changes to your veterinarian can facilitate more accurate diagnoses and quicker treatments.
Behavioral Changes
Behavioral changes are another key indicator of feline hepatitis. A normally playful and active cat may exhibit signs of withdrawal, becoming less interactive and more prone to hiding.
These changes can signal discomfort or pain, prompting owners to seek veterinary help. Paying attention to your cat's routine can provide valuable insights into their overall health status.
Diagnostic Approaches
Veterinarians often rely on blood tests and imaging techniques to diagnose feline hepatitis accurately. Elevated liver enzyme levels in blood samples can indicate liver inflammation or damage. Imaging, such as ultrasounds, allows veterinarians to visualize liver size and structure, assisting in identifying abnormalities like lesions or blockages.
Once diagnosed, treatment options may vary depending on the underlying cause of the hepatitis. Timely diagnostic intervention increases the chances of successful treatment and recovery.
Cat Bilirubin Levels
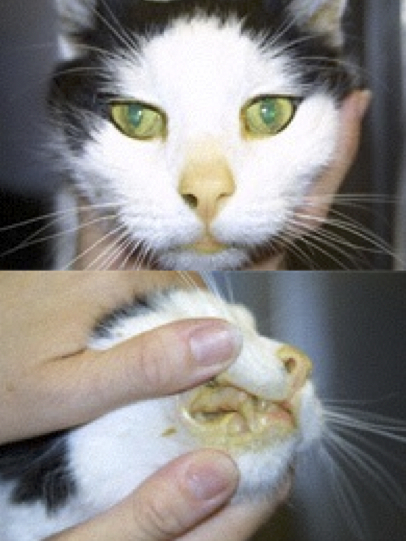
Cat bilirubin levels are integral to understanding jaundice and liver function. Bilirubin is a waste product formed during the breakdown of red blood cells. Its role in diagnosing liver issues cannot be overstated, as abnormal levels can indicate serious health concerns.
Understanding Bilirubin Types
There are two primary types of bilirubin: unconjugated (indirect) and conjugated (direct). Unconjugated bilirubin is produced when hemoglobin degrades, while conjugated bilirubin is processed by the liver and excreted.
Elevated levels of unconjugated bilirubin may indicate hemolytic anemia or liver dysfunction, whereas high levels of conjugated bilirubin typically suggest liver disease or bile duct obstruction. Monitoring these levels is crucial in diagnosing conditions associated with jaundice.
Clinical Significance of Bilirubin Testing
Testing bilirubin levels is a standard part of evaluating liver function in cats. A simple blood test can provide vital information about the liver's ability to process this waste product.
Vets will analyze the results in conjunction with clinical signs and other lab findings to determine appropriate interventions. Regular screenings may assist in identifying liver issues early, allowing for a better prognosis.
Managing Bilirubin Levels
Management of elevated bilirubin levels typically revolves around treating the underlying cause. Depending on the diagnosis, treatment may involve medication, dietary changes, or more invasive procedures for issues like bile duct obstruction.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle for your cat, including a balanced diet and regular vet check-ups, can aid in keeping bilirubin levels within a healthy range.
Feline Jaundice Treatment

The treatment of feline jaundice focuses on addressing the underlying cause while managing symptoms. Since jaundice itself is not a disease, but a symptom of various conditions, treatment plans can vary widely.
Immediate Veterinary Care
If jaundice is suspected, immediate veterinary care is critical. Your veterinarian will conduct a thorough examination, perform blood tests, and possibly recommend imaging studies to determine the root cause of elevated bilirubin levels.
Early veterinary intervention can significantly improve treatment outcomes, as certain conditions are more easily managed when caught early. Delayed treatment could lead to irreversible damage, particularly in the case of liver disease.
Treatment Options
Treatment options can vary greatly depending on the underlying cause of jaundice. For instance, if liver disease is diagnosed, a common approach may include dietary changes, medications designed to protect the liver, or corticosteroids to reduce inflammation.
In cases of bile duct obstruction, surgical intervention may be necessary to relieve the blockage. Alternatively, if hemolytic anemia is the culprit, treatment may focus on immunosuppressive therapy or managing underlying infections.
Supportive Care
Alongside targeted treatments, supportive care plays a vital role in managing jaundice in cats. Ensuring hydration through intravenous fluids, nutritional support via specialized diets, and pain management can significantly improve a cat’s recovery process.
Regular follow-ups and monitoring of liver function tests post-treatment can help track progress and adjust treatment plans accordingly. Many cats can recover well with appropriate and timely care.
Liver Failure in Cats
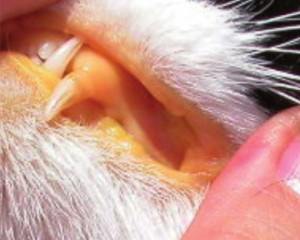
Liver failure in cats represents a severe progression of liver disease, often culminating in life-threatening conditions. Understanding the implications of liver failure can empower pet owners to act quickly if their feline friends show concerning signs.
Causes of Liver Failure
Liver failure can arise from numerous sources, including toxins, infectious diseases, and metabolic disorders. Any factor that severely damages liver tissues can eventually lead to failure, making it paramount for pet owners to be vigilant about their cat's health.
Environmental toxins, such as certain plants or chemicals, pose significant risks. Infections like feline infectious peritonitis (FIP) can also compromise liver function, leading to severe repercussions. Awareness of these factors aids in prevention and early detection.
Symptoms of Liver Failure
Symptoms of liver failure can be varied and may escalate quickly. In addition to jaundice, you may observe signs of severe lethargy, sudden weight loss, changes in behavior, or gastrointestinal disturbances like vomiting and diarrhea.
Another concerning symptom is ascites, where fluid accumulates in the abdominal cavity, causing swelling. As the condition progresses, neurological symptoms may arise due to toxin buildup, including disorientation or seizures.
Seeking Veterinary Help
If any signs of liver failure manifest, immediate veterinary assistance is crucial. Testing will typically involve comprehensive blood panels to assess liver function and imaging to identify structural issues.
Treatment may require hospitalization, including intravenous fluids, nutritional support, and medications aimed at stabilizing the condition. Although liver failure can be life-threatening, timely intervention can significantly impact survival outcomes.
Preventing Jaundice in Cats

While not all cases of jaundice can be prevented, certain proactive measures can substantially reduce risks associated with liver disease and related conditions.
Regular Veterinary Check-ups
Routine veterinary visits are essential for early detection of potential health issues. Regular examinations allow veterinarians to monitor your cat's overall health, including liver function.
Blood tests can provide insight into liver enzyme levels long before symptoms appear. Early detection of rising liver enzymes can lead to preventive measures before conditions worsen.
Proper Nutrition and Weight Management
A balanced diet is fundamental in maintaining liver health. High-quality cat food, specifically formulated for their nutritional needs, can prevent obesity and support liver function.
Managing your cat's weight through portion control and regular exercise is crucial. Obesity is a significant risk factor for developing liver disease, so maintaining a healthy lifestyle is imperative.
Avoiding Toxins
Minimizing exposure to environmental toxins is another essential preventive measure. Familiarize yourself with common household items toxic to cats, including certain plants, foods, and chemicals.
Creating a safe environment can significantly reduce the risk of chemical ingestion, which could lead to liver damage and subsequently jaundice.
Common Cat Liver Diseases

Understanding common cat liver diseases can help pet owners recognize symptoms and seek treatment in a timely manner. Knowledge of these conditions fosters a proactive approach to feline liver health.
Fatty Liver Disease
Fatty liver disease is one of the most prevalent liver conditions in cats, particularly among overweight individuals. It occurs when excess fat accumulates in the liver, impairing its function. Symptoms may include jaundice, vomiting, and lethargy.
Management often involves dietary adjustments, encouraging weight loss, and, in some cases, hospitalization for intensive nutritional support.
Cholangitis
Cholangitis is an inflammatory condition of the bile ducts, often presenting with symptoms such as jaundice and abdominal pain. Diagnosis typically involves imaging and bloodwork, with treatment focusing on antibiotics and anti-inflammatory medications.
Hepatic Lipidosis
Hepatic lipidosis arises when a cat stops eating for an extended period, leading to fat mobilization and liver accumulation. This condition can be life-threatening if not treated promptly.
Reintroducing feeding gradually, often through tube feeding, and supporting overall liver function are crucial components of treatment.
Conclusion

Jaundice in cats represents a complex interplay of various underlying health issues, predominantly associated with liver function. Recognizing the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is vital for responsible pet ownership.
By staying informed and observant, cat owners can take proactive steps towards preventing jaundice and associated liver diseases, ultimately enhancing their feline companions' quality of life. Regular veterinary care, appropriate nutrition, and awareness of harmful substances can significantly mitigate risks, ensuring a healthier, happier cat.
0 comment
Be the first to comment