Free Shipping On All Orders Over $150.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Canine Hip Dysplasia in dog
Hip dysplasia in dogs is a prevalent condition that affects their quality of life and mobility. This hereditary ailment stems from the improper formation of the hip joint, leading to discomfort and pain for our furry friends. As dog owners and enthusiasts, it's crucial to understand the various aspects surrounding this disorder, including its symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
Hip Dysplasia in Dogs: What Is It?

Hip dysplasia is a genetic condition characterized by the abnormal formation of the hip joint in canines. The joint, which should fit snugly, becomes loose due to poor development during a dog's early growth stages. This lack of proper alignment results in excessive movement, putting strain on the joint and causing inflammation, arthritis, and chronic pain.
The disease commonly manifests during the developmental phases of a dog's life, particularly between four to twenty-four months of age. However, signs may not always appear until the dog reaches maturity or even old age. Larger breeds such as Great Danes, Labrador Retrievers, and Saint Bernards are particularly predisposed to this condition, while smaller breeds tend to experience it to a lesser extent.
The Genetic Component

The primary cause of hip dysplasia in dogs is genetic. If a dog's parents carry the genes responsible for inducing this condition, there is a significant chance that their offspring will inherit it. Selective breeding practices can be beneficial in mitigating these risks, but they cannot eliminate them entirely.
Moreover, other factors such as rapid weight gain during puppyhood, the diet provided, and overall activity levels can exacerbate the problem. Owners should consider these elements seriously to prevent the onset of this challenging disorder.
Developmental Factors

In addition to genetics, environmental factors also play a significant role in the development of hip dysplasia. The physical structure of the pelvis, nutritional influences, and exercise habits all contribute to the likelihood of developing this condition.
Feeding puppies high-calorie diets can lead to accelerated growth, contributing to joint problems. Conversely, inadequate exercise can weaken muscles around the joint, leading to instability and further complications. Thus, a balanced approach to nutrition and activity is essential during a dog’s formative years.
Common Breeds at Risk
Certain dog breeds are more susceptible to hip dysplasia than others. Generally, large and giant breeds experience higher rates of occurrence. Some common breeds with a high prevalence of hip dysplasia include:
- Great Danes
- Saint Bernards
- Labrador Retrievers
- Rottweilers
While mixed breeds may also develop this condition, purebred dogs often face a greater risk, especially those bred without attention to health screening practices.
Symptoms of Hip Dysplasia in Dogs

Recognizing the symptoms of hip dysplasia in dogs is critical for timely intervention and treatment. Early detection can significantly influence a dog's long-term health and comfort.
Symptoms can vary depending on the severity of the condition and may evolve over time, so vigilance is essential. Below are some of the most notable canine hip dysplasia symptoms.
Decreased Activity Level
One of the most apparent signs of hip dysplasia is a reduced willingness to engage in physical activities. Dogs that once enjoyed playful outings may suddenly prefer lying down or resting instead.
As the condition progresses and joint pain intensifies, your dog may hesitate to participate in activities they previously relished. Observing changes in behavior can provide valuable insights into your dog’s health status.
Difficulty Standing Up
Another common indication of hip dysplasia is difficulty when standing up after lying down. Affected dogs may struggle to rise, appearing stiff or awkward.
This symptom is often accompanied by noticeable discomfort, as dogs may take time to adjust before moving normally. If you notice your dog having trouble getting up, it's vital to consult a veterinarian for a thorough evaluation.
Limping and Stiffness
A dog with hip dysplasia may exhibit limping, especially after exercising. This limping may be intermittent and can become more pronounced after physical activity.
Additionally, stiffness in the hind legs can make it difficult for dogs to navigate stairs or jump into vehicles. The lameness may fluctuate; thus, consistent observation is key to recognizing these changes.
Common Signs of Canine Hip Dysplasia

Beyond the major symptoms mentioned above, certain signs can indicate the presence of hip dysplasia in dogs. Recognizing these signs enables prompt diagnosis and treatment.
Unusual Gait
Dogs suffering from hip dysplasia often display unusual walking patterns. You may observe a swaying gait where the pelvic area rocks side-to-side as the dog moves.
The hind limbs may appear closer together, making the dog look bow-legged. Monitoring your dog's gait can help identify any irregularities indicative of hip or joint issues.
Muscle Atrophy
Muscle wasting or atrophy can result from prolonged inactivity due to pain. Dogs with hip dysplasia may show decreased muscle mass in their hindquarters as they avoid using these muscles to prevent discomfort.
This atrophy can further compound mobility issues, creating a vicious cycle that aggravates the condition.
Joint Pain
Joint pain may manifest as whimpering or whining, especially when the affected area is touched. Dogs might react negatively to pressure or manipulation around the hip region.
If your dog displays signs of discomfort, it’s essential to seek veterinary assistance immediately to address the underlying causes effectively.
Causes of Hip Dysplasia in Dogs
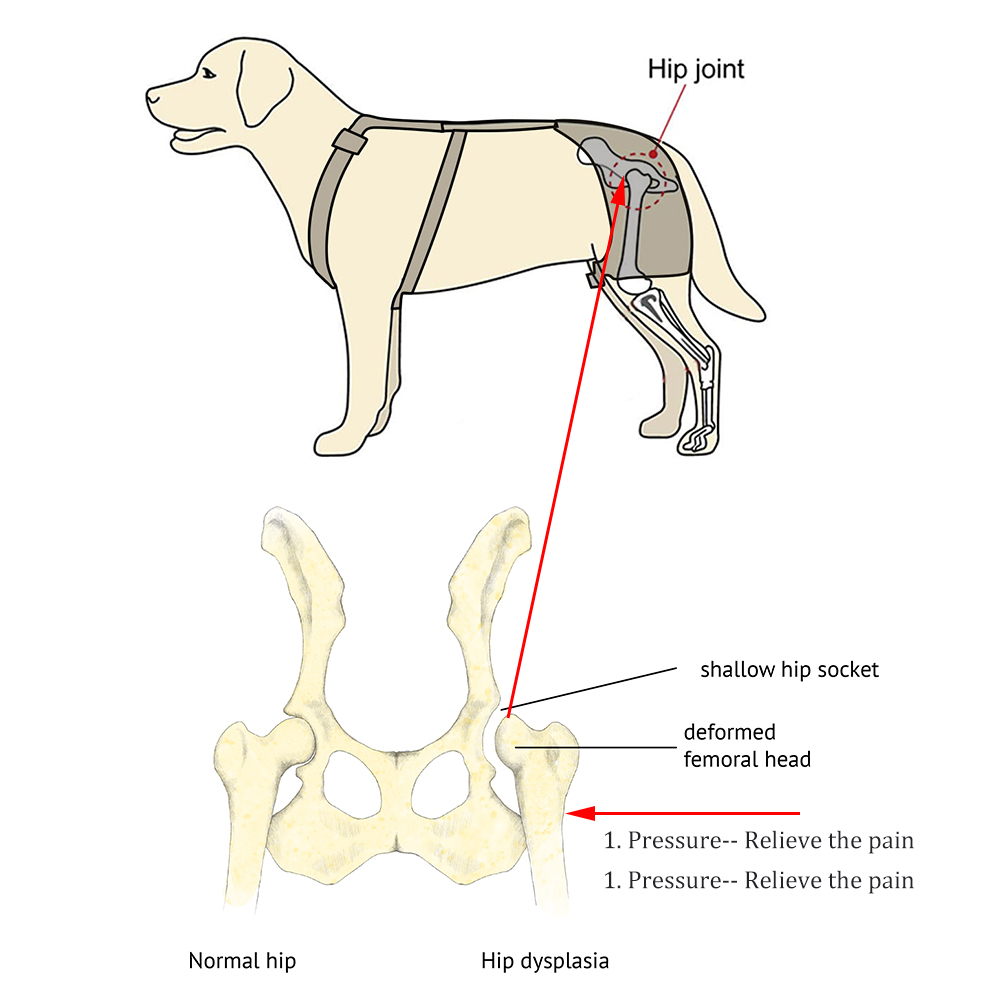
While genetics plays a significant role in determining whether a dog will develop hip dysplasia, several environmental factors exist that can exacerbate the condition. Understanding these causes equips dog owners with the knowledge necessary to mitigate risks.
Genetic Predisposition
As previously mentioned, hip dysplasia is primarily hereditary. If a dog's parents have a history of this condition, it increases the chances of their offspring developing similar issues.
Ethical breeding practices involve selecting for sound hips through screening programs to reduce the incidence of dysplasia. Responsible breeders prioritize health over appearance, ensuring future generations have the best chance of avoiding severe conditions like hip dysplasia.
Weight Management
Obesity is a significant contributing factor to joint problems, including hip dysplasia. Excess weight puts added stress on an already compromised joint, increasing pain and accelerating degeneration.
Maintaining a healthy weight through appropriate diet and regular exercise is crucial to decreasing the likelihood of exacerbating hip dysplasia symptoms.
Activity Levels
Both excessive exercise and a sedentary lifestyle can contribute to joint problems. While puppies need exercise to develop strong muscles and joints, they require supervised, controlled activities.
Engaging in high-impact sports too soon or allowing unrestrained play can lead to injuries. On the flip side, insufficient movement leads to weakened musculature, resulting in instability and further complications.
Diagnosing Hip Dysplasia in Dogs

To diagnose hip dysplasia in dogs, veterinarians employ various methods, including physical examinations, imaging tests, and medical history assessments. Accurate diagnosis is vital to determine the severity of the condition and formulate appropriate treatment plans.
Physical Examination
The first step in diagnosing hip dysplasia involves a comprehensive physical examination by a veterinarian. During this process, the veterinarian will assess the dog's range of motion, palpate the joints for abnormalities, and observe the dog's gait.
Signs of pain, discomfort, or limited mobility will guide the vet towards identifying potential issues. Your veterinarian may also evaluate your dog’s overall health, considering factors such as weight and muscular condition.
X-ray Imaging
X-rays are one of the most critical diagnostic tools used to identify hip dysplasia conclusively. These images allow veterinarians to visualize the structural integrity of the hip joint, revealing any malformations or signs of arthritis.
Radiographs can highlight joint space narrowing, subluxation, and bone spurs, providing comprehensive insights into your dog's condition. Such information is crucial for devising targeted treatment strategies.
Medical History Assessment
Alongside physical examinations and imaging tests, a detailed medical history is imperative when diagnosing hip dysplasia in dogs. Providing information about your dog’s previous injuries, activity levels, and dietary habits can greatly assist your veterinarian.
Understanding any family history of hip dysplasia can further inform the diagnostic process, as hereditary factors play a significant role in the condition's manifestation.
Treatment for Hip Dysplasia in Dogs

Treatment options for hip dysplasia in dogs vary based on the severity of the condition and the individual dog's needs. Approaches may include non-invasive measures, medications, or surgical interventions.
Medication and Supplements
For many dogs, medication can effectively manage pain and inflammation associated with hip dysplasia. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly prescribed to alleviate discomfort and improve mobility.
Additionally, joint supplements containing glucosamine, chondroitin sulfate, and omega fatty acids may support cartilage health and reduce inflammation, promoting better joint function.
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
Physical therapy can play a significant role in managing hip dysplasia symptoms. Tailored rehabilitation programs can strengthen supporting muscles around the hip joint, enhancing stability and mobility.
Various techniques, including hydrotherapy and massage, can reduce pain and improve joint flexibility. Engaging a certified canine rehabilitation therapist can ensure your dog receives appropriate care tailored to their specific condition.
Surgery Options
In severe cases where conservative treatment fails to provide relief, surgical options may be considered. Surgical procedures include:
- Total Hip Replacement: This involves removing the damaged hip joint and replacing it with a prosthetic joint, offering significant improvements in mobility and pain management.
- Triple Osteotomy: A procedure designed to reposition the hip joint for better alignment and function, reducing pain and improving mobility.
Surgical decisions depend on multiple factors, including a dog’s age, weight, and overall health. Discussing the risks and benefits of each option with your veterinarian is crucial for making informed choices.
Triple Osteotomy: An Advanced Surgical Technique
Triple osteotomy surgery is a specialized procedure aimed at correcting hip dysplasia by realigning the hip joint. This advanced technique can significantly enhance a dog's quality of life, especially for younger dogs with moderate to severe dysplasia.
Procedure Overview
During the triple osteotomy procedure, the veterinarian makes incisions around the hip joint to access the femur and pelvis. The surgeon then cuts the bones, allowing them to be repositioned correctly. After achieving optimal alignment, they secure the bones in place using plates and screws.
This realignment redistributes weight and pressure evenly across the joint, reducing pain and improving function. While recovery usually involves careful monitoring and rehabilitation, many dogs experience substantial improvements post-surgery.
Postoperative Care
Post-surgery care is vital for ensuring successful recovery and long-term outcomes. Following the operation, your dog will likely require pain management and restrictions on activity levels.
Gradually introducing controlled exercises, along with follow-up appointments, helps monitor healing progress. Working closely with your veterinarian is essential to optimize recovery and reinforce positive habits that promote joint health.
Long-term Outcomes
The long-term success of triple osteotomy depends on various factors, including the dog's age, weight, and commitment to postoperative rehabilitation. Many dogs experience heightened mobility and reduced pain after this procedure, leading to enriched lives.
Owners must remain vigilant regarding their dog’s ongoing care post-surgery, from maintaining a healthy weight to incorporating appropriate exercise routines.
Preventing Hip Dysplasia in Dogs

Preventing hip dysplasia in dogs requires a proactive approach encompassing responsible breeding practices, proper nutrition, and an active lifestyle. Ensuring your dog enjoys a healthy, fulfilling life relies on understanding the significance of these preventive measures.
Responsible Breeding Practices
Choosing a reputable breeder is paramount when acquiring a new puppy. Reputable breeders conduct health screenings on their breeding stock, ensuring that they do not pass on genetic predispositions to hip dysplasia.
Evaluate breeders carefully, requesting documentation of health clearances and family histories. Engaging in this diligent process establishes a foundation for healthier future generations.
Optimal Nutrition
Providing a balanced diet tailored to your dog's specific needs plays a crucial role in preventing obesity and promoting joint health. Consult with your veterinarian to determine the best diet for your dog’s age, breed, and activity level.
Controlling portion sizes and avoiding overfeeding are essential steps in managing your dog's weight. Moreover, incorporating joint supplements can proactively support joint health.
Regular Exercise Routines
Maintaining an active lifestyle is vital for promoting strong muscles and joint health in dogs. Regular exercise should be age-appropriate and adjusted to consider your dog’s physical capabilities and limitations.
Avoiding high-impact activities during a dog’s developmental phase can significantly reduce the risk of injury. Instead, focus on low-impact exercises, such as controlled walks and swimming, that encourage muscle strengthening while minimizing stress on the joints.
Conclusion

Hip dysplasia in dogs is a complex condition that significantly impacts the lives of our beloved pets. Understanding its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options is crucial for responsible dog ownership. Through proactive measures such as responsible breeding, proper nutrition, and tailored exercise routines, we can work towards preventing this debilitating condition.
By staying informed and seeking veterinary guidance when needed, we can ensure that our furry companions lead happy, active lives free from unnecessary pain and discomfort.
0 comment
Be the first to comment