Free Shipping On All Orders Over $150.
Many Dog Owners Are Unaware of Canine Jaundice Disease
Canine jaundice symptoms are critical indicators of underlying health issues that every dog owner should be aware of. When your beloved pet shows signs of yellowing skin or eyes, it can be alarming and may indicate a serious condition affecting their liver function. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the various aspects of canine jaundice, shedding light on its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment options. Understanding these factors is vital for ensuring the well-being of your furry friend.
Canine jaundice symptoms

When dealing with canine jaundice symptoms, it’s essential to recognize them early on. The primary sign of jaundice in dogs is a noticeable yellow tint to the skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. This discoloration occurs due to an accumulation of bilirubin, a yellow pigment produced during the breakdown of red blood cells.
In addition to the yellowing, other symptoms may accompany jaundice. Owners might observe changes in behavior, such as decreased appetite or lethargy. You may also notice increased thirst, frequent urination, vomiting, and diarrhea. These signs are indicative of various dog health problems, particularly those related to liver dysfunction.
The appearance of jaundice can be distressing not only for the dog but also for the owners who witness their pet's discomfort. It's important to remain observant and proactive in addressing any concerning symptoms. Early intervention can significantly enhance the chances of recovery and improve the overall prognosis for your dog.
Recognizing early signs
Recognizing the initial signs of jaundice in dogs can make a world of difference. Apart from the obvious yellow coloration, keep an eye out for changes in behavior or energy levels. Dogs suffering from liver issues may exhibit uncharacteristic lethargy or reluctance to engage in their usual activities.
Monitoring your dog’s eating habits is equally important. If your normally enthusiastic eater suddenly seems disinterested in food or is eating significantly less, it could indicate an underlying problem. Additional signs include excessive panting or changes in bowel movements, which can further signal potential liver complications.
Being vigilant about these symptoms will empower you to take timely action when necessary. Regular veterinary check-ups can also help catch any emerging issues before they escalate into more severe conditions.
Importance of veterinary consultation
If you suspect your dog is exhibiting signs of canine jaundice symptoms, consulting a veterinarian promptly is crucial. Only a qualified professional can accurately diagnose the condition through a thorough examination and diagnostic tests.
During the visit, the vet will assess your dog's medical history and conduct various tests, including blood work, urinalysis, and possibly imaging studies. These evaluations will help determine the root cause of the jaundice and guide the appropriate treatment plan.
Remember, while some cases of jaundice may resolve with proper care, others may require more intensive interventions. Seeking immediate veterinary assistance can provide your pet with the best chance at recovery.
Dog liver disease
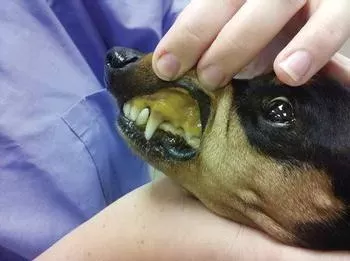
Dog liver disease encompasses a range of conditions that can affect the liver's ability to function correctly. The liver plays a vital role in metabolizing nutrients, detoxifying harmful substances, and producing essential proteins. When the liver suffers damage, it can lead to severe health complications, including jaundice.
Understanding the types of liver diseases that can affect dogs is essential. Some common forms include hepatitis, cirrhosis, and liver tumors. Each condition presents unique challenges and requires specific management strategies.
It's crucial for dog owners to familiarize themselves with the potential risk factors contributing to liver disease. Factors such as genetic predisposition, exposure to toxins, infections, and age can all influence liver health. By being aware of these risks, you can take proactive measures to safeguard your dog's well-being.
Common liver diseases in dogs
There are several dog liver diseases that owners need to watch for. One common condition is infectious hepatitis, caused by a virus that attacks liver cells. Symptoms typically include fever, abdominal pain, and jaundice.
Cirrhosis, on the other hand, is a chronic condition resulting from long-term liver inflammation or damage. It leads to scar tissue formation, impairing the liver's function over time. Dogs with cirrhosis may experience weight loss, vomiting, and behavioral changes.
Liver tumors, whether benign or malignant, can also impact liver function. Symptoms can vary depending on the tumor's size and location, making early detection essential for effective treatment.
Understanding these common liver diseases and their associated symptoms can equip you with the knowledge needed to monitor your dog's health effectively.
Risk factors for liver disease
Identifying the risk factors for liver disease can help you take preventive measures. Certain breeds, such as Labrador Retrievers, Doberman Pinschers, and Yorkshire Terriers, may have hereditary predispositions to liver conditions.
Environmental factors play a significant role as well. Exposure to toxins found in household chemicals, certain plants, and even some medications can adversely affect liver health. Ensuring your dog has a safe environment free from hazardous substances is vital in minimizing their risk.
Age is another crucial factor; older dogs tend to be more susceptible to liver diseases due to cumulative exposure to risk factors over time. Regular check-ups become increasingly important as dogs age, allowing for early detection of any potential issues.
By understanding these risk factors, you can work towards creating a healthier living environment for your canine companion.
Yellow skin in dogs
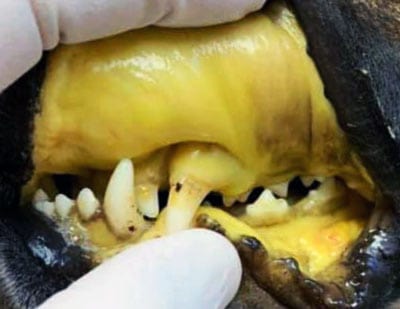
One of the most visible yellow skin in dogs is jaundice, which can serve as a key indicator of underlying health issues. The yellow color results from elevated levels of bilirubin, which accumulates when the liver fails to process it effectively.
Notably, jaundice is not a disease itself but rather a symptom of an underlying condition that affects the liver. Therefore, recognizing when your dog exhibits yellow skin can help guide you toward seeking appropriate veterinary care.
Beyond the skin, jaundice can also affect the eyes and gums, leading to discoloration that can be alarming for dog owners. It is essential to understand that not all yellowing indicates jaundice; other factors, such as dietary influences, could contribute to changes in coloration.
Distinguishing jaundice from other conditions
While yellow skin in dogs is primarily associated with jaundice, it's important to differentiate this condition from other ailments that may cause similar appearances. For example, certain infections or disorders can result in pigmentation changes that may confuse dog owners.
Additionally, bile duct obstructions can lead to similar symptoms. However, these conditions may present different accompanying symptoms. Vigilance in observing your dog's overall health will help you draw connections between various signs and reach a more accurate conclusion.
If you notice yellowing in your dog's skin or mucous membranes, don't hesitate to consult a veterinarian for clarification and possible testing. Understanding the broader context surrounding jaundice can lead to more effective decision-making regarding your dog's health.
The psychological impact on owners
Witnessing your dog develop yellow skin can evoke feelings of anxiety and uncertainty among pet owners. Pets are cherished members of our families, and seeing them in distress can take a toll on our emotional well-being.
It’s normal to feel overwhelmed when faced with health issues concerning our furry friends. Educating yourself about potential conditions and available treatments can alleviate some stress, providing you with valuable information to discuss with your veterinarian.
Moreover, engaging in supportive communities of fellow dog owners can foster a sense of camaraderie, helping you cope with your dog's illness. By sharing experiences and advice, you can navigate this challenging journey together.
Jaundice in dogs causes
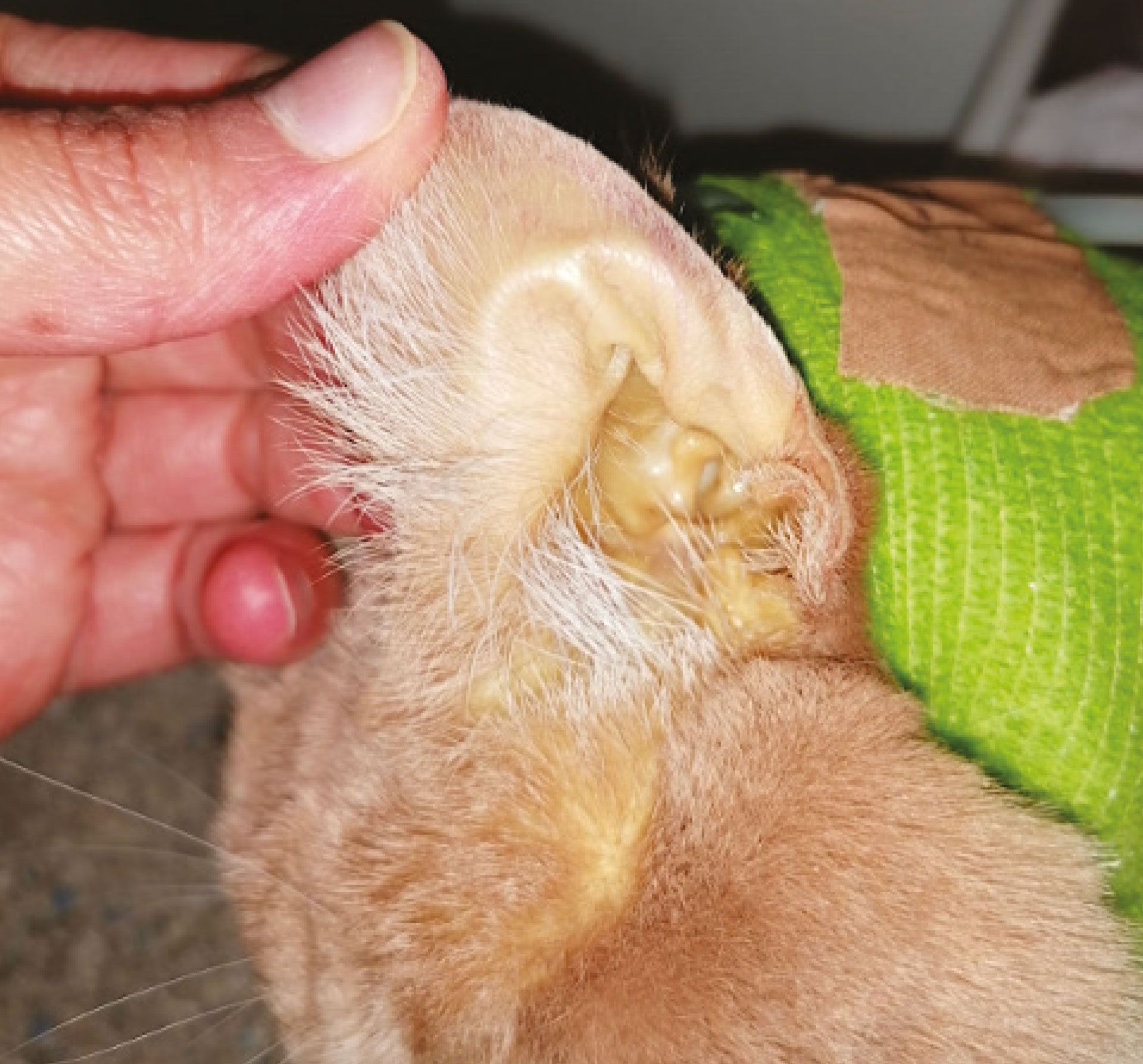
Understanding the jaundice in dogs causes is essential for effective management and treatment. As previously mentioned, jaundice arises from an excess of bilirubin in the bloodstream, often due to liver dysfunction. However, there are various underlying factors that can contribute to this condition.
Bacterial infections, viral hepatitis, and parasites can all trigger liver inflammation, leading to elevated bilirubin levels. Other causes include toxins from medications or environmental exposure, autoimmune diseases, and even certain metabolic disorders.
Identifying the correct cause of jaundice is crucial since treatment approaches may differ significantly depending on the underlying issue. A comprehensive veterinary evaluation will typically involve blood tests, imaging, and potential biopsies to pinpoint the precise cause.
Infections as a potential cause
Several infections can lead to jaundice in dogs. Canine infectious hepatitis is one such example, caused by a virus that primarily targets liver cells. Dogs infected with this virus may exhibit symptoms ranging from fever to abdominal pain, along with the characteristic yellowing of the skin.
Leptospirosis, another bacterial infection, can also impact liver function. This zoonotic disease spreads through contaminated water or soil, making it crucial for owners to ensure their dogs remain in safe environments.
Conversely, parasitic infections such as heartworm can contribute to liver issues as well. Heartworms can cause significant damage to the liver and other organs, especially if left untreated. Being aware of the potential infectious causes of jaundice can help you take preventative measures, such as vaccines or regular screenings.
Toxic exposure and its consequences
Toxic exposure represents another significant cause of jaundice in dogs. Household chemicals, certain plants, and even specific human foods can pose severe risks to your pet's health. For instance, ingestion of xylitol, a common artificial sweetener, can lead to rapid liver failure.
Moreover, medications that are safe for humans can sometimes have detrimental effects on dogs. Always consult your veterinarian before administering any drugs to your pet, and never adjust dosages without professional guidance.
If you suspect your dog has been exposed to a toxic substance, acting quickly is paramount. Immediate veterinary intervention can make a substantial difference in outcomes and may even save your dog's life.
Dog health problems
The presence of dog health problems can often culminate in symptoms like jaundice. Identifying these health issues early on is vital for effective intervention. Chronic conditions, infections, and injuries can all contribute to liver dysfunction, leading to elevated bilirubin levels.
Some common health problems that may precipitate jaundice include diabetes, pancreatitis, and Cushing's syndrome. Each of these conditions can exert pressure on the liver, impeding its capacity to filter toxins and produce essential substances.
Being informed about potential health problems can empower you to make decisions that positively influence your dog's quality of life. Proactive monitoring and regular veterinary visits are essential in safeguarding your canine companion’s health.
Chronic illnesses and their implications
Chronic illnesses can have far-reaching implications for a dog's liver health. Diabetes, for example, can lead to complications that strain the liver's functionalities over time. If left unmanaged, diabetic dogs may experience additional health challenges, including liver disease.
Pancreatitis, characterized by inflammation of the pancreas, can also impact liver function. Dogs suffering from this condition may experience digestive difficulties and a higher risk of jaundice due to the interconnected nature of liver and pancreatic health.
Being open and communicative with your veterinarian regarding any existing health issues can facilitate better management of your dog's overall well-being. Together, you can develop a tailored healthcare plan that addresses their specific needs.
The importance of prevention
Preventing dog health problems is often easier than treating them after they have developed. Regular veterinary check-ups can catch potential issues before they escalate, allowing for timely intervention.
Maintaining a balanced diet tailored to your dog's specific needs is essential in promoting good health. Quality nutrition supports immune function and helps reduce the risk of chronic conditions that may affect liver health.
Furthermore, staying informed about breed-specific health concerns can aid in preventing certain conditions from arising. By understanding your dog's unique risks and being proactive in their care, you can contribute to a longer, healthier life for your furry friend.
Liver failure in dogs

Liver failure in dogs is a grave and often life-threatening condition that often manifests through jaundice. When the liver is unable to perform its functions, it can lead to severe health repercussions, including nutrient deficiencies and toxin buildup.
Acute liver failure can result from sudden exposure to toxins or infection, whereas chronic liver failure develops over time due to ongoing damage. Regardless of the type, recognizing the signs early can significantly improve your dog's outcome.
The severity of liver failure varies based on the extent of damage and the underlying cause. While some dogs may recover with immediate intervention, others may suffer irreversible damage that necessitates ongoing care.
Symptoms of liver failure
Symptoms of liver failure in dogs can be subtle initially, but they often progress rapidly. In addition to jaundice, affected dogs may experience symptoms like vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal swelling. Behavioral changes, such as increased lethargy or agitation, may also occur.
As the condition worsens, dogs may exhibit signs of neurological distress, such as confusion or seizures. This occurs when toxins build up in the bloodstream due to the liver's failure to filter effectively.
Recognizing these symptoms early can make a profound difference in treatment options and potential outcomes. If you see any combination of these signs, seek veterinary care immediately.
Treatment options for liver failure
Treatment options for liver failure in dogs depend on the underlying cause and the extent of damage. In cases where toxins are identified, prompt removal of the offending substance may be possible, allowing the liver a chance to heal.
Supportive care is critical, including intravenous fluids, nutritional support, and medications to manage symptoms. In instances of chronic liver failure, dietary modifications and supplements may be required to assist liver function.
In advanced cases, surgical interventions may be necessary to address underlying conditions contributing to liver failure. Each case is unique, so collaborating closely with your veterinarian can lead to a more personalized treatment approach.
Diagnosing jaundice in dogs
Diagnosing jaundice in dogs requires a systematic approach involving a combination of clinical evaluation and laboratory tests. A veterinarian will begin by taking a detailed medical history of your dog, followed by a physical examination to assess their overall health.
Once the vet identifies potential symptoms consistent with jaundice, a series of diagnostic tests will be performed to ascertain the underlying cause. Blood tests, urinalysis, and imaging studies are commonly utilized to gather valuable information.
Understanding how veterinarians diagnose jaundice and its causes can give dog owners greater insight into the care process and help them to feel more empowered during veterinary visits.
Physical examination
During the physical examination, the veterinarian will look for classic signs of jaundice, such as yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes. They will also evaluate the liver's size and consistency by palpating the abdomen, checking for any unusual masses or abnormalities.
Additional observations may include assessing your dog's hydration status, body temperature, and overall demeanor. Each of these factors contributes to forming a clearer picture of your dog's health.
The physical exam serves as a foundational step, guiding the veterinarian's subsequent decisions regarding additional testing and possible treatment plans.
Laboratory tests
Laboratory tests are critical components of diagnosing jaundice in dogs. Blood work can reveal vital information about liver function, including enzyme levels indicative of liver damage or inflammation.
Urinalysis will help identify the presence of bilirubin in urine, which can further confirm jaundice. Elevated levels of bilirubin are typical in cases of liver disease, signaling that the liver is not processing waste correctly.
Imaging techniques, such as ultrasound or X-rays, can provide additional insights into liver structure and detect abnormalities such as tumors or blockages. Collectively, these tests enable veterinarians to narrow down the root cause of jaundice and formulate an appropriate treatment strategy.
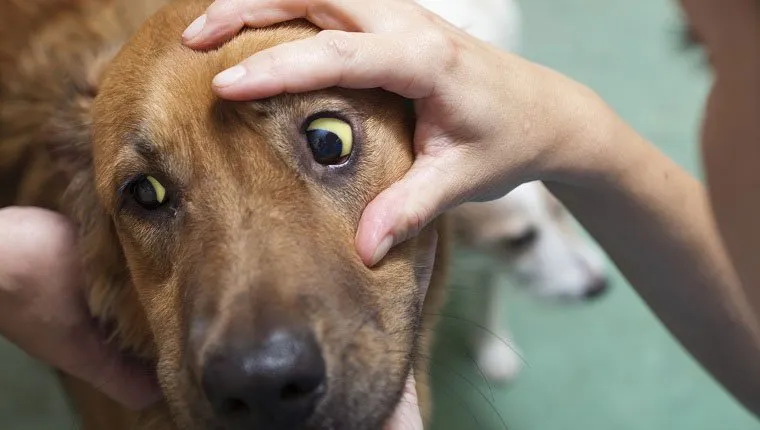
Canine bilirubin levels
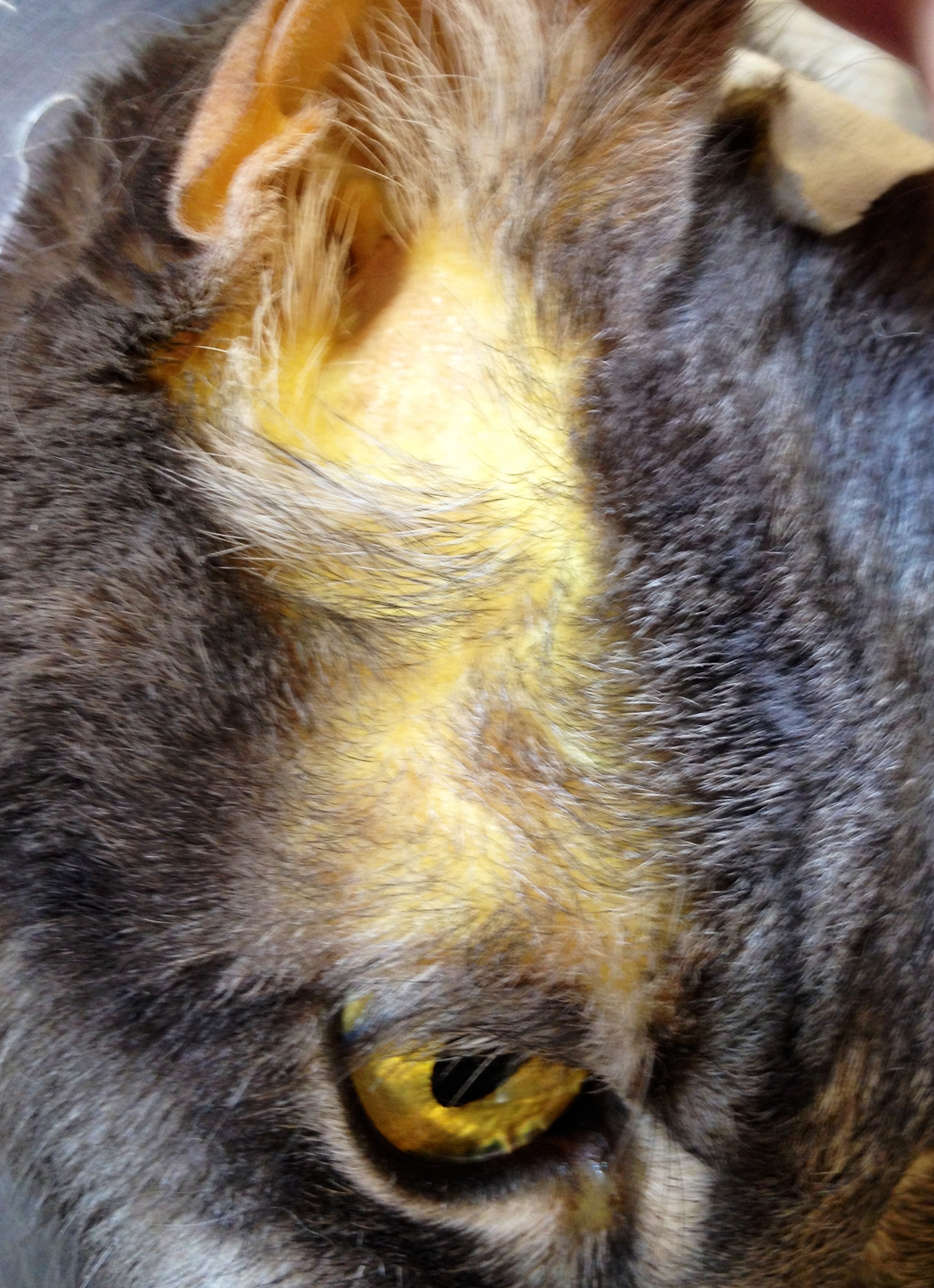
Canine bilirubin levels are crucial indicators of liver health and function. Bilirubin is a yellow pigment formed during the breakdown of red blood cells, and its levels in the bloodstream can inform veterinarians about potential liver issues.
In healthy dogs, bilirubin levels remain within a specific range. Elevated bilirubin levels indicate that the liver is struggling to process this waste product, often resulting in jaundice. Monitoring these levels is essential for diagnosing and managing liver conditions effectively.
Veterinarians routinely check bilirubin levels during blood tests as part of their diagnostic process, enabling them to gain valuable insights into your dog's liver function.
Interpreting bilirubin levels
Interpreting canine bilirubin levels requires an understanding of both total and direct bilirubin readings. Total bilirubin reflects the sum of both unconjugated (indirect) and conjugated (direct) bilirubin in the bloodstream.
Unconjugated bilirubin is typically elevated in hemolytic anemia cases or when there is a disruption in red blood cell breakdown. Conversely, conjugated bilirubin elevation suggests liver malfunction or obstruction in bile flow.
These interpretations guide veterinarians toward identifying the primary source of jaundice, ensuring efficient treatment plans are implemented.
Monitoring bilirubin levels
Regularly monitoring canine bilirubin levels is crucial, especially for dogs diagnosed with liver issues. Regular blood tests allow for tracking changes in bilirubin levels over time, offering insights into treatment effectiveness and potential disease progression.
Establishing baseline bilirubin levels can also aid in detecting any new or recurring health issues. Pet owners should maintain open communication with their veterinarians regarding any observed changes in their dog's condition, facilitating timely interventions when necessary.
By understanding the significance of bilirubin levels, dog owners can become active participants in their pet's health journey.
Dog jaundice treatment

When it comes to dog jaundice treatment, the approach largely depends on the underlying cause of the jaundice. A comprehensive evaluation by a veterinarian sets the foundation for an effective treatment plan tailored to your dog’s specific needs.
Generally, treatment aims to address the underlying condition causing jaundice while providing supportive care to help the liver heal. Depending on the diagnosis, options may range from medication and dietary changes to more complex procedures.
Understanding the treatment landscape for jaundice can help dog owners feel more confident navigating their pet’s care journey.
Medications and therapy
Medications form a significant aspect of dog jaundice treatment. Anti-inflammatory drugs may be prescribed to reduce liver swelling, while antibiotics can combat infections contributing to the liver dysfunction.
In cases of liver disease, antioxidant supplementation can help protect liver cells from damage and promote healing. Nutritional therapy may also be employed, focusing on a balanced diet tailored to support liver function.
Ongoing communication with your veterinarian is key to adjusting treatment plans as needed and ensuring your dog receives the best possible care.
Dietary modifications
Dietary modifications are an integral part of managing jaundice in dogs. A specialized diet rich in high-quality protein sources, low in copper, and easy to digest can significantly benefit the liver.
Veterinarians often recommend feeding smaller, more frequent meals to ease the digestive burden on a compromised liver. Additionally, incorporating ingredients known for supporting liver health, such as milk thistle and omega-3 fatty acids, can enhance your dog's recovery.
Always consult with your veterinarian before making any significant dietary changes, as they can provide tailored recommendations based on your dog's individual health needs.
Signs of liver issues in dogs
Recognizing signs of liver issues in dogs is critical for timely intervention and treatment. While jaundice serves as a prominent indicator, there are numerous other symptoms pet owners should be aware of.
Changes in appetite and energy levels, as discussed earlier, can signal liver dysfunction. Moreover, behavioral changes such as increased irritability or restlessness may also occur alongside physical symptoms.
Monitoring your dog's overall health and noting any shifts in behavior can lead to quicker diagnostics and better outcomes when liver issues arise.
Gastrointestinal symptoms
Gastrointestinal symptoms frequently accompany signs of liver issues in dogs. Vomiting and diarrhea may indicate that the liver is struggling to filter toxins effectively, leading to gastrointestinal upset.
Dogs may also experience changes in bowel movements, such as pale stools or dark urine, which may reflect alterations in bilirubin processing. Paying attention to these changes can provide valuable insights into your dog's liver health.
If you notice persistent gastrointestinal symptoms, a veterinary consultation can help identify potential underlying causes and facilitate appropriate treatment.
Neurological changes
Neurological changes may manifest when liver function declines significantly. As toxins accumulate in the bloodstream, they can affect brain function, leading to symptoms such as confusion, seizures, or disorientation.
Pet owners should be vigilant for signs of distress or abnormal behavior, as these may indicate escalating liver issues. In severe cases, hepatic encephalopathy may develop, posing a serious threat to your dog's health.
Immediate veterinary attention is paramount if you observe any neurological symptoms, as timely intervention can help prevent further complications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding canine jaundice symptoms and their underlying causes is vital for every dog owner. By recognizing the signs of liver dysfunction and seeking prompt veterinary care, you can significantly improve your dog’s chances of recovery.
Throughout this journey, it is essential to stay informed about the various aspects of your dog’s health. Prevention, early detection, and treatment are key components to ensuring a long and healthy life for your furry companion.
Your vigilance and dedication to your dog’s well-being can make all the difference. By fostering open communication with your veterinarian and remaining engaged with your pet’s health needs, you can navigate the complexities of canine care with confidence. Together, let’s pave the way for a brighter future for your beloved canine friend.
0 comment
Be the first to comment